Past projects
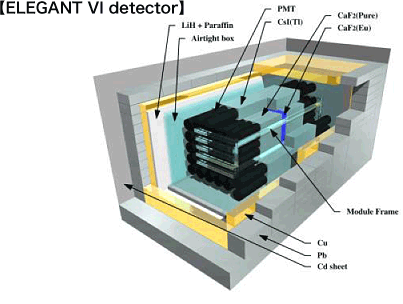
ELEGANT IV experiment
This is the system which is the basis of the CANDLES project. It uses CaF2 crystals doped with Eu (ordinarily indicated as CaF2 (Eu)) to search for dark matter and study double beta decay, and has achieved the most sensitive measurement for double beta decay of 48Ca. It is the basic research that later became CANDLES.
The CaF2 (Eu) signal is detected by a photomultiplier tube (PMT), using pure CaF2 crystals that have not been doped with an activator (CaF2 (pure)) as light guides on both sides. CaF2 (pure) also acts as a scintillator, and is a veto counter in the direction of the PMT. A 5×5 array of 25 of these combinations was fabricated, and the surrounding area covered with CsI (Tl) detectors to achieve active shielding in 4π directions. This structure was able to achieve a background-free condition and delivered very remarkable results. The concept of the CANDLES experiment was developed based on this success.
The detector is also surrounded by ordinary passive shielding such as lead or copper, and the tanks of a boric acid water solution (omitted from the figure) are put around the outside as a neutron shield. The completed system was installed at the underground Oto Cosmic Observatory, an underground location equivalent to 1,400 m of water shielding.
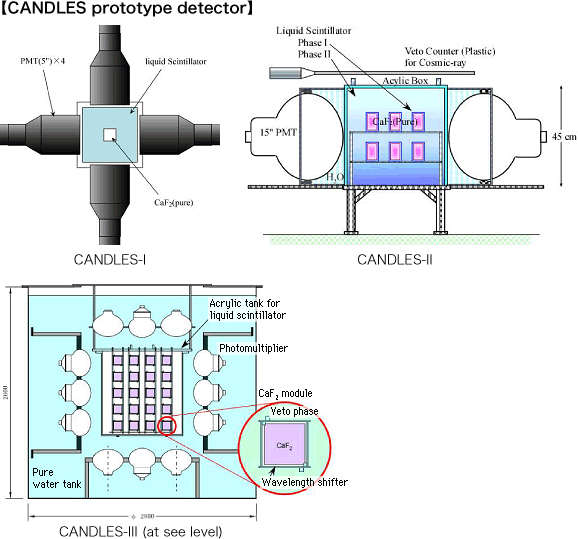
CANDLES prototype experiment
This is a detector system which was used to verify the basic CANDLES principles.
A pure CaF2 crystal un-doped with an activator was immersed in a liquid scintillator, and scintillation light detectors (CANDLES-I) were created around it using four 5-inch PMT. The signals were identified by utilizing the difference in time constants between the scintillation light from the CaF2 crystals (1 μs) and the light from the liquid scintillator (only 10 ns). This verified that it was possible to actively shield the background radiation from outside the detector and from the PMT. A study which immersed two CaF2 crystals was also performed, and showed that it was possible to identify the crystal where the scintillation light was emitted.
This verified that the CANDLES system would work even when the large number of crystals was used. Four large, nearly full-size, PMTs (tube diameter 15 inches) were used to construct the system which measured multiple crystals simultaneously (CANDLES-II). With this system, it was possible to install up to 18 crystals.
Next was a detection system which immersed 60 10×10×10 cm3 CaF2 crystals (each 3.2 kg, total 190 kg) in liquid scintillator for measurement (CANDLES-III at sea level). Research and development were performed above ground at Osaka University.